The cost reduction in Solar PV and the incentives rolled out in several countries and across the world are the two main factors for the rapid adoption of this technology by the householders. The incentives that are mostly based on feed-in-tariffs and net-metering schemes provided opportunities to householders to save on their electricity bills through the generation of solar energy.
However, these incentives, and as every incentive aiming to promote and accelerate the adoption of new technologies, are gradually phasing down (1-5). This means that all surplus energy generated by your solar system will be exported back to the grid without being paid for that. Some might argue that they have a large consumption, so all generated solar energy will be used locally. But have you ever wondered when your solar produces the most energy? It occurs during midday when most people are not at home (e.g., due to work, school, etc.). Because of this, most of the generated Solar is not consumed locally and is, therefore, fed back (for free) to the grid. This essentially means a lot of free and green energy being wasted. Let’s try to see an example using real consumption data from a UK household to make things more transparent.

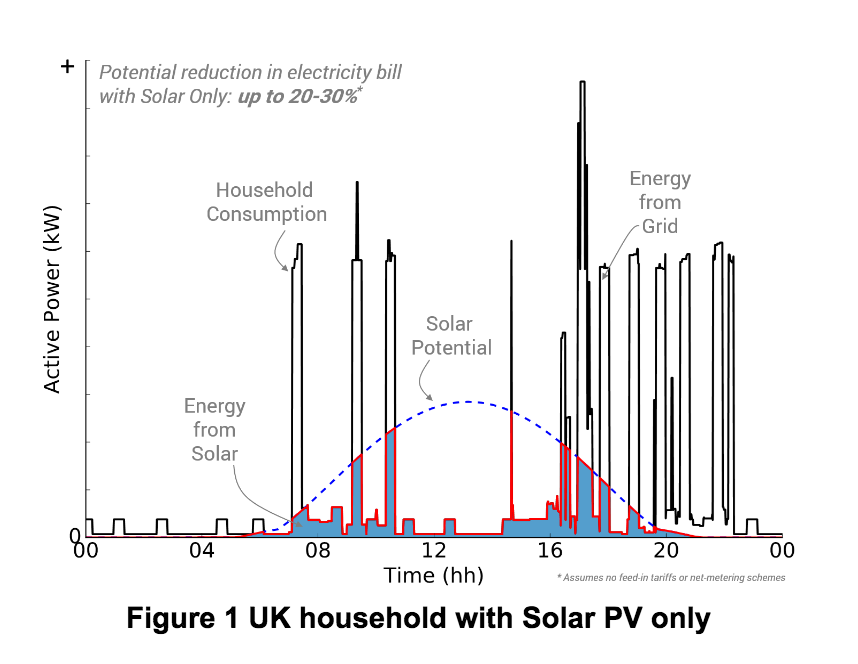
Figure 1 shows a real UK household consumption behavior during a sunny summer weekday. The black line indicates the household consumption, and the blue dashed line shows its solar PV generation potential. As can be seen, most of the generation happens during the midday where the consumption happens to be lower than the early morning hours and night. Nonetheless, when the consumption co-exists with solar generation, the consumption is partly (or entirely) provided by the Solar system. While this operation can reduce the household’s electricity bill up to 30%, there is a significant amount of free and green solar energy being unused. Unused energy could be stored and used at a later time rather than exporting it into the grid. This is exactly where Watts Battery’s modular energy storage system can help you make the most out of your solar energy and further reduce your electricity bill.
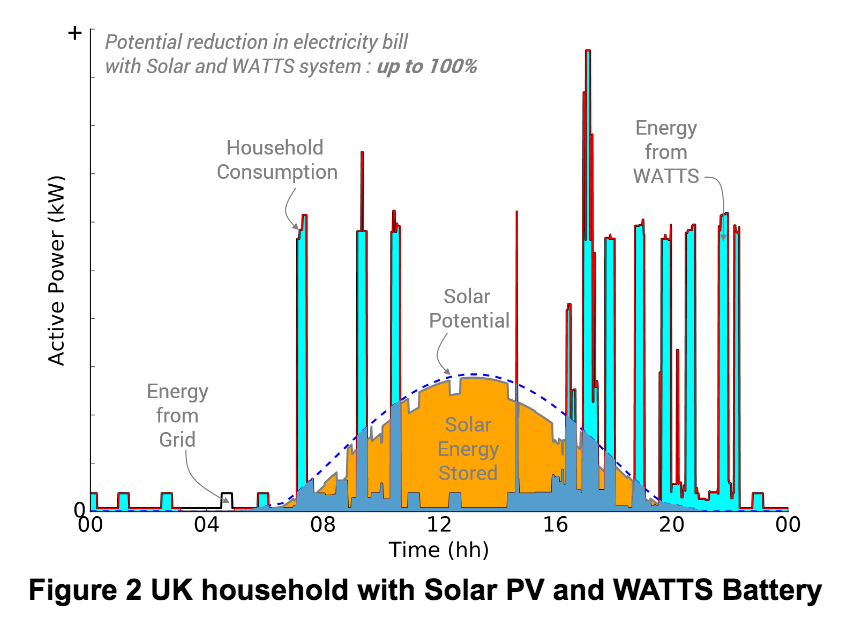
Considering the same scenario, let’s see how WATTS modules can bring more value to the household using Figure 2, which now assumes 3 WATTS modules. As it can be observed, our modules can help store all the unused Solar generated energy (see orange color) and supply the household demand during the night or moments where the household demand power is larger than the solar power (see cyan color). This behavior not only can help to reduce electricity bills (up to 100%) significantly, but it can potentially help households increase their energy independence through self-consumption while reducing their carbon emissions.
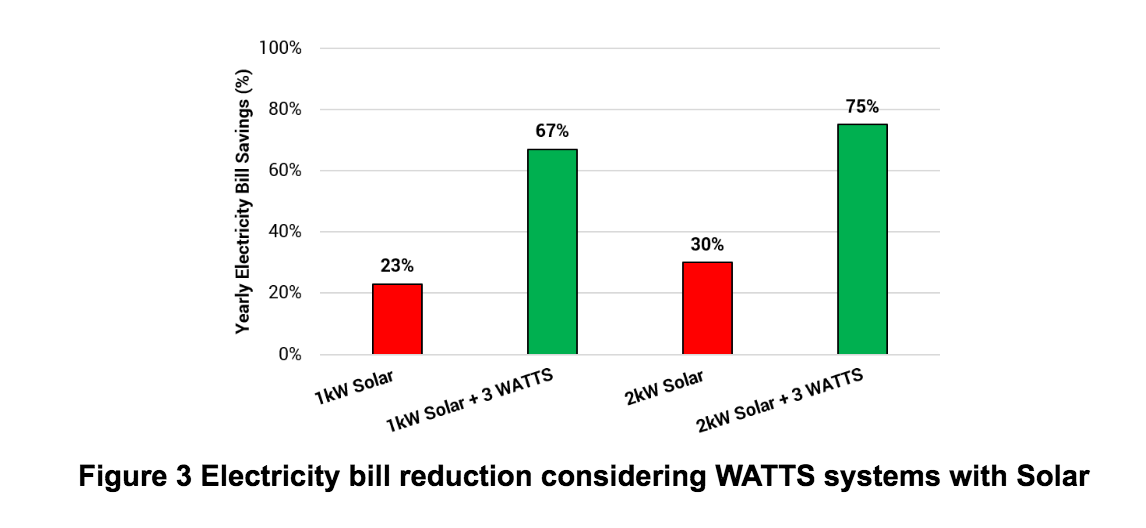
While the above examples allow visualizing the operation of WATTS modules with Solar, to understand the true value brought to households thoroughly, we have performed a study considering a year-long analysis using consumption and generation data from a real UK household to extract the level of energy savings that can be achieved with our systems. Figure 3 shows the yearly electricity bill reduction of a UK household considering the cases of having solar only (red bars) and solar combined with WATTS modules (green bars).

Considering Solar, 2 different sizes 1 and 2kWp systems are used along with a stack of 3 WATTS modules (4.5kW/3.6kWh). The analysis highlights that while increasing your solar PV system’s size, the financial benefit (i.e., bill reduction) is limited (savings up to 30%). However, when the Solar PV system is combined with the WATTS, the financial benefit doubles with potential electricity bill savings reaching 75%.
Do you want to start saving on your electricity bill? Just drop us a line at
Article by Andreas T. Procopiou, Chief Product Officer


